
【Population-based meta-analysis of chloroquine: informing chloroquine pharmacokinetics in COVID-19 patients】
The outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has quickly become a global pandemic since December 2019. Chloroquine is recommended to treat COVID-19 by the National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China and issued as emergency use authorization (EUA) by The US Food and Drug Administration. Prof. Yan Xiaoyu from CUHK Pharmacy, cooperating with researchers from Drug Clinical Trial Center of Beijing Peking University Third Hospital and China Pharmaceutical University, developed a population pharmacokinetics (PK) model to characterize the Chloroquine pharmacokinetics (PK) in COVID-19 patients using a population-based meta-analysis approach.
Understanding the Chloroquine PK in COVID-19 patients is essential to study its exposure–efficacy/safety relationship and provide a basis for a possible dosing regimen optimization. With sparse PK samples available, a population PK model allows addressing critical gaps in experimental PK data, which was pulled from literature and a first clinical trial conducted in COVID-19 patients.
Model-based simulation shows that the concentrations under the currently recommended dosing regimen are below the safety margin for side effects, which suggests that these dosing regimens are generally safe. The derived population PK model should allow for the assessment of pharmacokinetics–pharmacodynamics (PK-PD) relationships for Chloroquine when given alone or in combination with other agents to treat COVID-19.
Full research paper published in the European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7665884
【基於人群的薈萃分析:研究氯喹在COVID-19病人中的藥代動力學特徵】
自2019年12月以來,2019年冠狀病毒疾病(COVID-19)爆發已迅速成為全球大流行病。中華人民共和國國家衛生委員會建議將氯喹用於治療COVID-19,美國食品和藥物管理局也將氯喹作為緊急使用授權(EUA)藥物。香港中文大學藥劑學院閆曉宇教授與北京大學第三醫院藥物臨床試驗中心和中國藥科大學的研究人員合作,基於人群薈萃分析方法建立了群體藥代動力學模型,用於表徵氯喹在COVID-19病人中的藥代動力學特徵。
理解氯喹在COVID-19病人中的藥代動力學特徵對於認識其暴露-效應/安全關係十分重要,并且能為優化可能的給藥方案提供依據。群體藥代動力學模型能夠利用少量的PK樣本解決實驗PK數據之間的鴻溝,氯喹PK數據來源於文獻和第一個在COVID-19病人中進行的臨床試驗。
基於模型的模擬結果顯示,當前推薦給藥方案下的濃度低於產生副作用的安全範圍,證明了給藥方案的安全性。建立的群體藥代動力學模型可應用於評估氯喹在單獨給藥或聯合給藥治療COVID-19的藥代動力學與藥效學(PK-PD)關係。
相關論文已於國際學術期刊European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology發表: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7665884
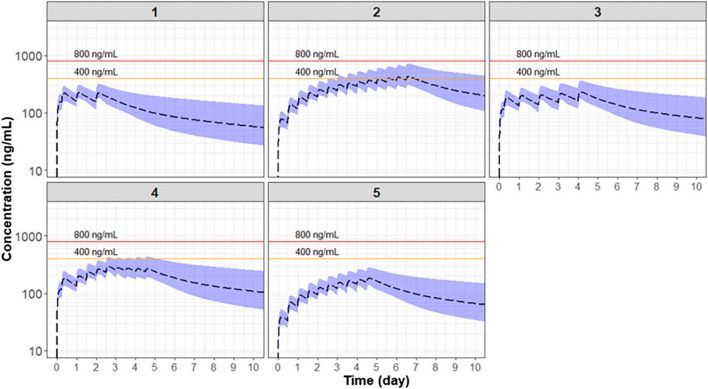
Simulations of chloroquine PK under various dosing regimens. The black dashed line represents the 50th percentile and the shaded area represents the range between 5th and 95th percentile. The solid line represents the safety concentration threshold of 400 mg/ml and 800 mg/ml


